5 Hands-On Lab: Data Annotation
Goal
This hands-on lab session is designed to give participants practical experience in data annotation for deep learning. Participants will apply the methods, tools, and best practices discussed in the previous session, working directly with datasets to annotate data effectively.
Key Elements
Use of annotation methods and tools, direct dataset interaction
Choose your own adventure(s)
In this section, we’ll provide some links, basic information, and suggested starter activities for a variety of annotation tools available today. Have a look and get your hands dirty!
Note: You’ll need some images to annotate in each case. Feel free to use any relevant images you might already have, or just do a web search and find something interesting. Of course, when experimenting with the web-based annotation platforms, be sure not to upload anything personal, private, or otherwise sensitive.
Ideally, you’ll cover:
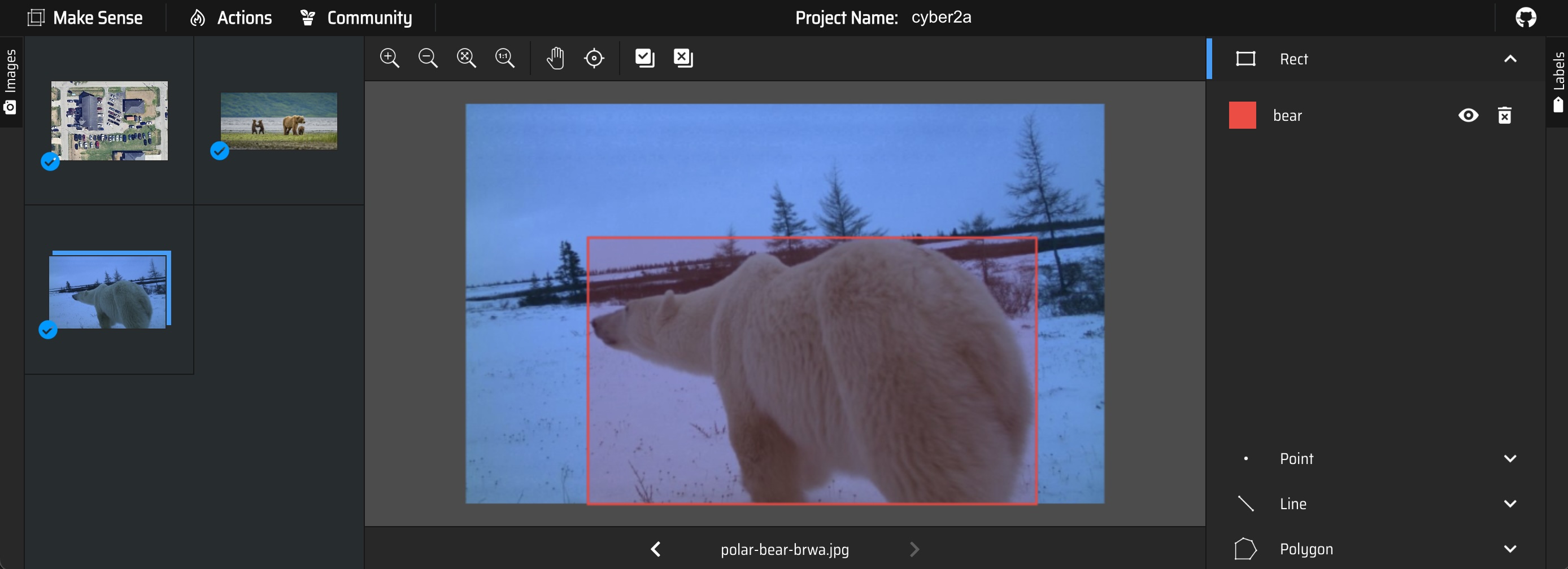
5.1 Adventure: Make Sense
- MakeSense.ai is a simple, single-user, browser-based image annotation app
- Supports annotation via bounding boxes, polygons, points, and lines
- Upload one or more images, apply/edit annotations, then export annotations
- Offers model-based semi-automated annotation with an accept/reject interface
- If you prefer, you can also grab the source code and run it locally using npm or Docker
Things to try
5.2 Adventure: Roboflow
- Roboflow offers a cloud-hosted, web-based platform for computer vision, including tooling for data annotation along with model training and deployment
- They offer a limited free tier, which does not offer any privacy (project and images are automatically public)
- Nice interface for doing annotations, managing artifacts, and managing the team
Things to try
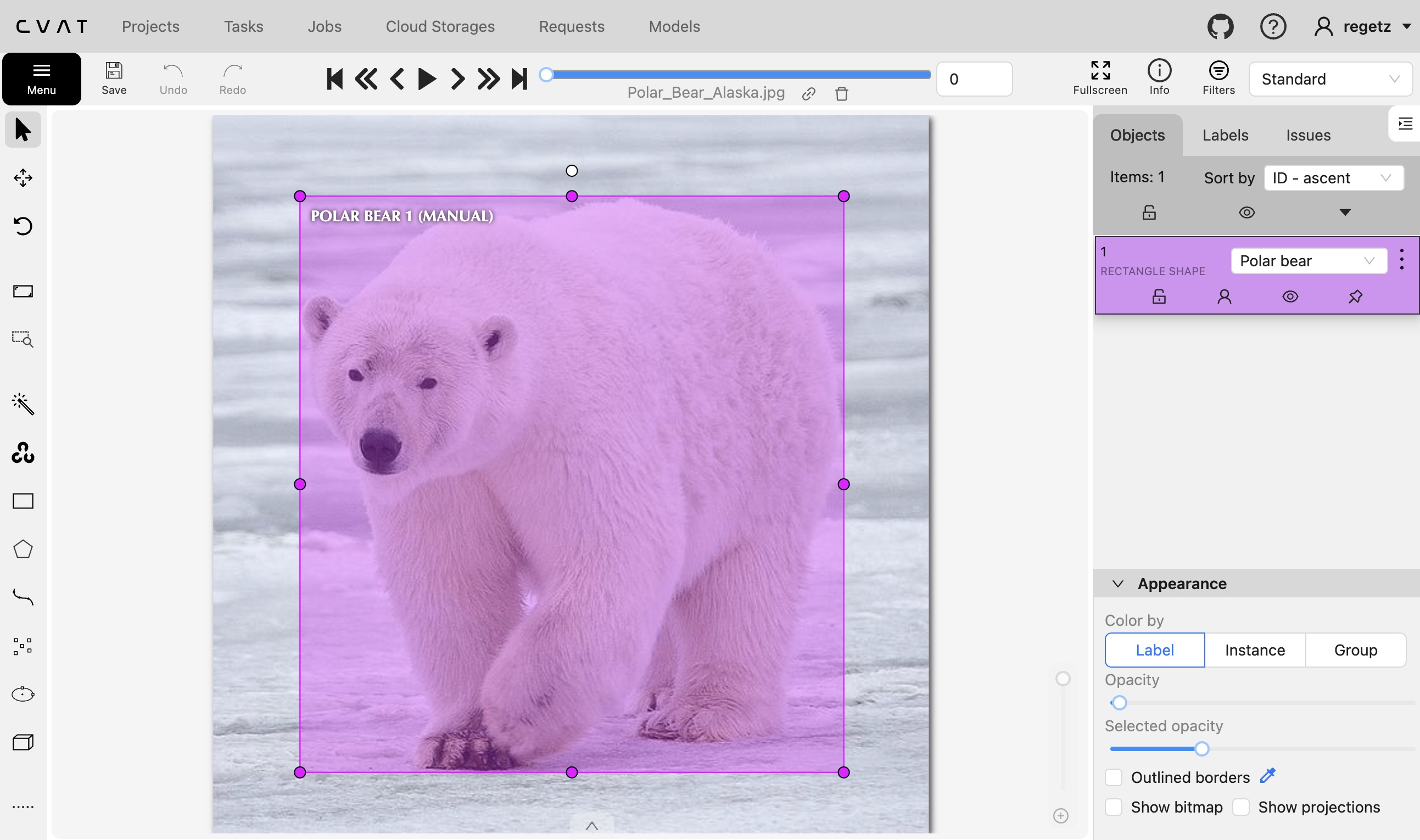
5.3 Adventure: CVAT
- CVAT can be used as a desktop application that you install & run on your own local computer or server.
- However, for today, consider creating your own (free) account for annotating using their hosted platform
- The V7 CVAT guide might be helpful.
Things to try
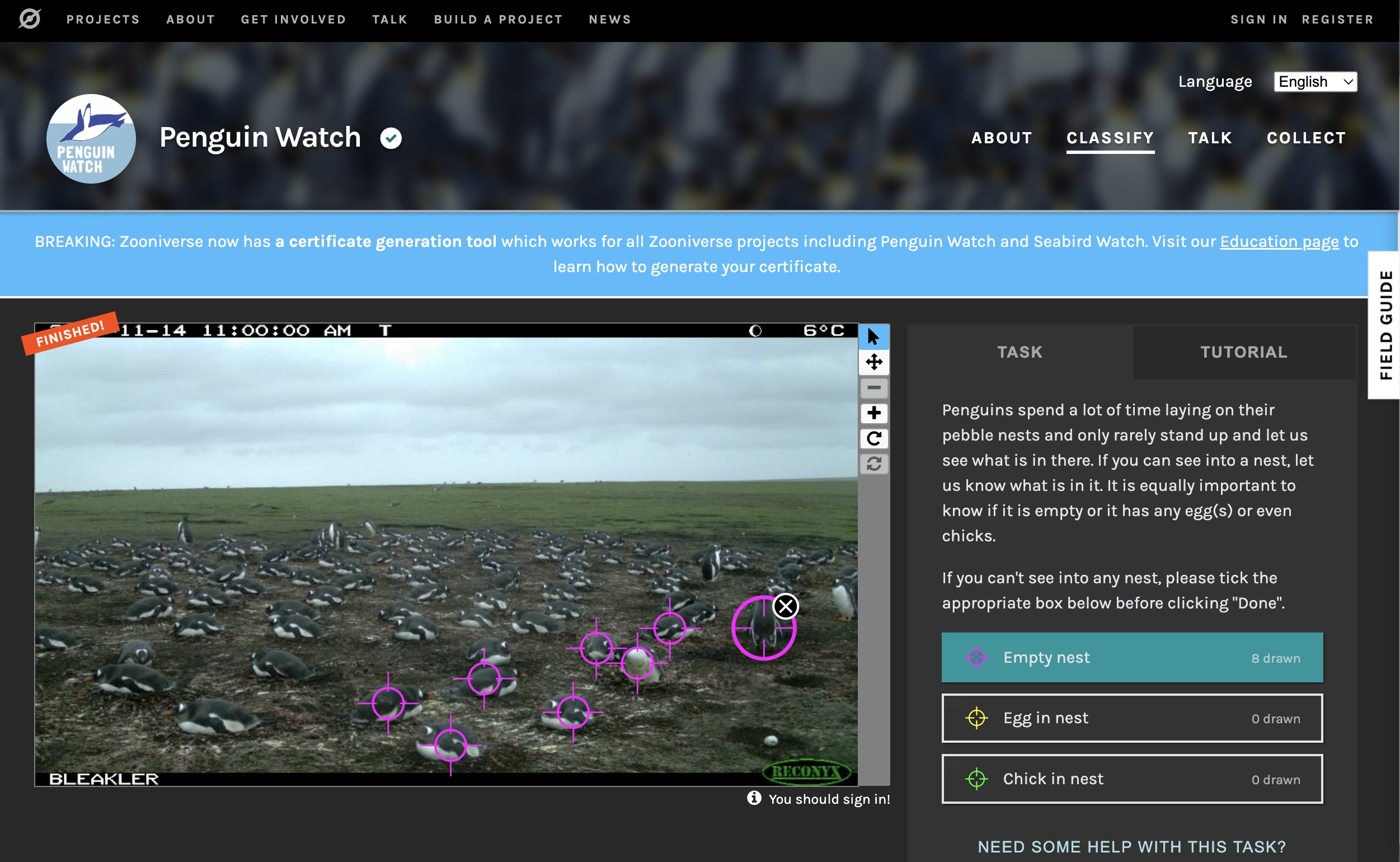
5.4 Adventure: Zooniverse
Zooniverse is a web-based community crowdsourcing platform for data annotation and digitization.
Things to try
5.5 Adventure: IRIS (Intelligently Reinforced Image Segmentation)
IRIS is a tool for doing semi-automated image segmentation of satellite imagery (or images in general), with a goal of accelerating the creation of ML training datasets for Earth Observation. The user interface provides configurable simultaneous views of the same image for multispectral imagery, along with interactive AI-assisted segmentation.
Unlike much of the ML we’ll encounter this week, the backend model in this case is a gradient boosted decision tree. The reason this works sufficiently well is that IRIS is geared toward segmenting multispectral imagery into a small number of classes, training from scratch on each image; the model is able to learn the correlation structure between features and labels by leveraging multiple features per pixel after the human-in-the-loop manually segments and labels pixels.
For more information, check out the YouTube video with the main creator, Alistair Francis.
Things to try
5.6 Adventure: Segment-Geospatial (samgeo)
This is an open-source tool that you can either install locally or run in JupyterLab (or Google Colab).
First, check out the online Segment Anything Model (SAM) demo. SAM was developed by Meta AI. It is trained as a generalized segmentation model that is able to segment (but not label) arbitrary objects in an image. It is designed as a promptable tool, which means a user can provide initial point(s) or box(es) that roughly localize an object within an image, and SAM will try to fully segment that object. Alternatively, it can automatically segment an entire image, effectively by self-promtping with a complete grid of points, and then intelligently merging the corresponding segments.
Today, SAM is used by numerous image annotation tools to provide interactive, AI-assisted segmentation capabilities.
One such tool is the segment-geospatial Python package, which provides some base functionality for applying SAM to geospatial data, either programmatically or interactively.
Note that in addition to using segment-geospatial directly using Python in a notebook or other environment, you can also play with SAM-assisted segmentation in QGIS and ArcGIS.
Things to try
5.7 Adventure: Label Studio
- Multi-type data labeling and annotation tool with standardized output format
- Works on various data types (text, image, audio)
- Has both an open-source option and a paid cloud service
- See the online playground
5.8 Other things to try
- VGG Image Annotator (VIA)
- Try a local installation?